Chestnut-backed Chickadee
General Description
With their white cheeks and dark caps and throats,Chestnut-backed Chickadees look much like Black-capped Chickadees. However the caps of Chestnut-backs are brown rather than black, and their backs, shoulders, and sides are a deep chestnut color. They are also slightly smaller than Black-capped Chickadees. Males, females, and juveniles share similar plumage.
Habitat
Chestnut-backed Chickadees favor dense, moist, coniferous forests. They can be found from the lowlands up to the tree line, wherever there is a wet, closed-canopy forest.
Behavior
During the breeding season Chestnut-backed Chickadees are territorial, but they join mixed-species flocks in winter. They forage by hopping along twigs and branches and gleaning their surfaces or by probing into bark crevices for food. They often hang upside-down to get at the undersides of branches and needles. They readily come to seed and suet feeders. Chestnut-backed Chickadees store food in the fall and retrieve it in winter.
Diet
Insects, spiders, conifer seeds, and berries make up most of these omnivores' diets. They also readily eat suet and birdseed supplied by humans.
Nesting
Much of the nesting biology of Chestnut-backed Chickadees is not well known. They are monogamous, and pairs may excavate their own nest cavity (in soft rotten wood) or may use an old woodpecker hole or other cavity, including artificial nest boxes. The female builds a foundation of moss, lichen, and other material within the nest cavity, and then adds a lining of soft hair. She incubates 6 to 7 eggs. Incubation length is not well known, but incubation times for most chickadee species are about two weeks. Both members of the pair tend the young, but details of nestling time and time to independence are not well known.
Migration Status
During some winters Chestnut-backed Chickadees in colder climates may wander short distances, mostly as a result of food shortages. For the most part, however, they are permanent residents.
Conservation Status
When Northwest coniferous forests are clear-cut, hardwoods are often the first trees to grow in their place. Thus, clear-cutting favors Black-capped Chickadees, which prefer deciduous vegetation, over the conifer-specialized Chestnut-backeds. Although the Breeding Bird Survey has not detected significant trends in Washington, and Christmas Bird Count data reflect an increase throughout the Northwest, Chestnut-backed Chickadees have declined in the Seattle urban area. Audubon-Washington includes this species on its list of species-at-risk.
When and Where to Find in Washington
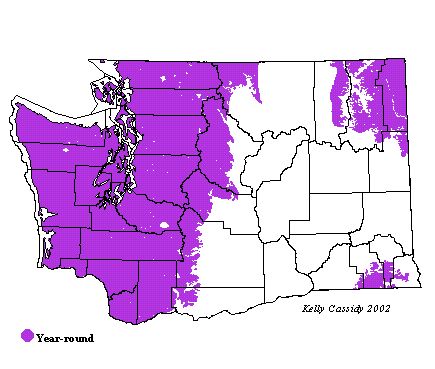
Chestnut-backed Chickadees are permanent residents in wet coniferous forests throughout the state. The majority of these habitats are in western Washington, where this bird is abundant, but some areas of eastern Washington provide suitable habitat as well. Chestnut-backeds are probably the most abundant chickadee species west of the Puget Trough and are the only chickadee just to the north on Vancouver Island, BC.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
| Puget Trough | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
| North Cascades | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C | C |
| West Cascades | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| East Cascades | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| Okanogan | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U | U |
| Canadian Rockies | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| Blue Mountains | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| Columbia Plateau |
Washington Range Map
North American Range Map